INTRODUCTION TO EDITORS
Definition
An editor is general-purpose system software, which can be used to enter and /or modify text, program, figures or data
Overview
of Editing Process:
All
interactive editors are computer systems program that allow user to create and
revise a target document. The term document includes objects such as computer
programs, text equations, tables, diagrams, line art and photographs, anything
one might find on a printed page.
The interactive editing process
is accomplished with the following tasks:
The part of the target document that needs to be manipulated is viewed.
The
document is first displayed in the required format.
Using the necessary designed tools, the document is modified.
The view is updated appropriately and saved.
TYPES
OF EDITORS
Editors
are broadly classified as:
I. Line
Editors
A line editor edits a line at a time. Not
more than one line can be edited at a time. Line number is used to accept the
line for editing. A line editor may have the following features:
There
are different line-editors working on different operating system. Some of them
are:
CP/M System: EDIT
DOS
System: EDLIN
UNIX
System: ED
Line
editors are always pointing to a single line in a file called the current line.
When an existing file is accessed, the last line is made the current line so
that the text can be appended easily. During editing session, the contents of a
file are altered in a temporary buffer until creating or correcting the text is
complete. When the existing file is edited, a copy of that file is placed in the
buffer and changes are made to the copy. The changes have no effect on the
original file until the buffer input is written into the file.
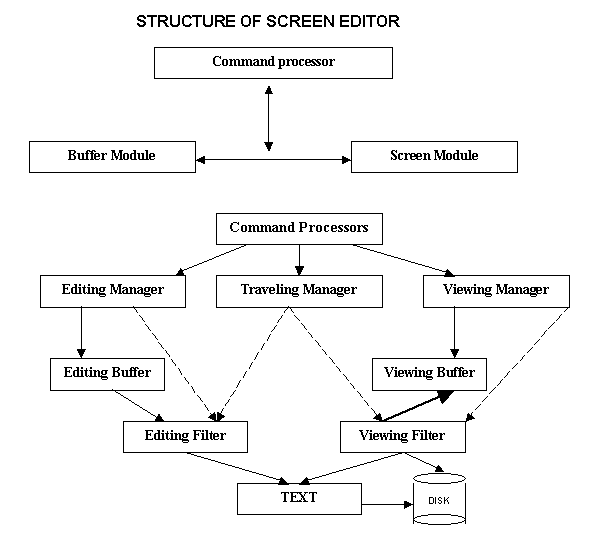
In a screen editor, the user has
control over the entire file. The user is free to make any changes and see them
immediately on the screen or in the file. There are different commands to edit
the text. Some of he commands are as follows:
Cursor Movement:
Cursor Left:
Cursor moves left by one character without deleting any character.
Cursor Right: Cursor moves right by one character without deleting
any character.
Cursor Up: Cursor moves up by one line without deleting any
character.
Cursor Down: Cursor moves down to the next line without deleting a
character.
Word Right: Cursor moves to the next word to the right if it exists.
Word Left: Cursor moves to the next word to the left if it exists.
Cursor to the start of the file: The cursor is moved to the top left
of the screen and it will be the first page from where the text is displayed.
Cursor to the end of file: The cursor moves to the bottom right of
the screen and this screen will be the last part.
Cursor to the top of the screen: The cursor moves to the top left of
the present screen.
Cursor to the bottom of the screen: the cursor moves to the bottom
right of the present screen.
Cursor to start of the line: The cursor moves to the start of the
present line.
Cursor to the end of line: The cursor moves to the end of the
present line.
Page Up: Cursor moves to the previous page of display if it exists.
Page Down: Cursor moves to the next page of display if it exists.
Delete:
These
commands is used to remove the characters.
A Line:
The present line (where the cursor is at present) is completely deleted.
To the end of the line: From the present cursor position till the
end of line the characters are deleted.
To the beginning of line: From the present cursor position till the
beginning of the line the line characters are deleted.
Word Right: To the right of the cursor a word is deleted.
Word Left: To the left of the cursor a word is deleted.
Search:
These
commands are used to search for a string.
Find:
This is a command to place the cursor where the requested string is matched. If
the string does not exist "not found" message is displayed.
Find and replace: This command is used to find the requested string
and replace with the new string. If the requested string is not found, an error
message is displayed.
File Services:
These commands are related to the file in
secondary device.
Copy File:
This command is used to copy a file from one to another file. The second file is
a new file.
Delete File: The mentioned file is deleted from the secondary device
using this command.
Append File: This command copies one-file contents to another. The
second file contents will add after the first file content.
Save File: The file contents of the buffer are stored in the
secondary device
with
the filename.
Save As: The contents of the buffer are saved into the secondary
device with the new filename
Load: The contents of the file mentioned are moved into the buffer
and is put into viewing buffer.
Pick: If more than one file is loaded into the buffer, it is
possible to view the one required by picking the file from the set of opened
files.
New: Data typed can be stored into the secondary file by giving a
name to it.
There are different screen
editors available:
Some of them are:
VI
Editor, Emac Editor - (Unix O.S.)
Norton
Editor, Edit - (DOS)
Screen
editor displays from one to many lines of text. Different varieties of screen
editors are possible, based on the types of user interface used. They are:
1. Full screen window text editor:
This editor uses the complete area of the display in the text mode. The user can
make changes at the point of cursor.
2. Multiple Window Text Editor:
The editor divides the screen into two or more windows to display different
files in each window. The user can edit the text in one window at a time, but
can see the contents of all the windows simultaneously. The user depending on
the requirements can alter the size of the window.

A graphic oriented editor is
mainly used for creating and modifying picture. Graphic display allows control
over every pixel (picture element) displayed on the CRT and typically display
480 rows x 640 pixels. Higher the display pixels, higher will be the resolution
of the picture. There are different monitors available for higher resolutions.
These displays extend the possibilities for user interfaces and can also support
accurate imaging to produce on screen display that it facsimiles (exact copies)
of type set documents.
Some of the features of graphic
editor are:
A
few examples are:
Corel Draw
AutoCAD
Paint Brush
ZAP works